When we feel unfocused, distracted or mentally drained, we often blame lack of focus and willpower. Is it the attitude that needs to be blamed or is there a hidden culprit behind all the unproductivity? Well, a simple nutrient deficiency might be holding you back. Emerging studies suggest low magnesium levels could be silently sabotaging mental clarity.
An average adult requires 400 to 420 milligrams of magnesium per day. Magnesium is a vital mineral and supports over 300 biochemical reactions of the body. Beyond physical health, magnesium plays a key role in cognitive functioning and emotional balance.
 Why does magnesium matter to the brain?Magnesium supports multiple essential functions in the body and works as a master regulator. It helps balance neurotransmitters like GABA and glutamate, which are the brain's chemical messengers. It also modulates the stress hormone, cortisol, and prevents excessive spikes and promotes emotional resilience.
Why does magnesium matter to the brain?Magnesium supports multiple essential functions in the body and works as a master regulator. It helps balance neurotransmitters like GABA and glutamate, which are the brain's chemical messengers. It also modulates the stress hormone, cortisol, and prevents excessive spikes and promotes emotional resilience.
Beyond the brain, magnesium supports healthy blood flow by relaxing blood vessels. Healthy blood flow ensures efficiency. On a cellular level, magnesium is essential for producing the energy ‘currency’ of the cells, ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
What can be the sign of magnesium deficiency?Research shows magnesium deficiency can impair synaptic plasticity, which is the brain’s ability to form new connections. Synaptic plasticity directly affects learning and memory. Magnesium has also been associated with reducing the risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
 Maintaining adequate magnesium levels is crucial for cognitive health and its deficiency can affect in physical and mental ways:
Maintaining adequate magnesium levels is crucial for cognitive health and its deficiency can affect in physical and mental ways:
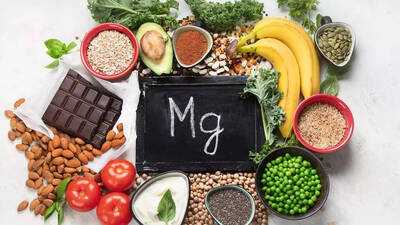 Meeting the daily magnesium requirement isn’t so complicated. Eating a variety of magnesium rich foods like leafy greens (mostly spinach), almonds, pumpkin seeds, black beans, dark chocolate or salmon, combined with mindful lifestyle habits can help maintain optimal levels of magnesium and support mood, energy, focus and overall health.
Meeting the daily magnesium requirement isn’t so complicated. Eating a variety of magnesium rich foods like leafy greens (mostly spinach), almonds, pumpkin seeds, black beans, dark chocolate or salmon, combined with mindful lifestyle habits can help maintain optimal levels of magnesium and support mood, energy, focus and overall health.
An average adult requires 400 to 420 milligrams of magnesium per day. Magnesium is a vital mineral and supports over 300 biochemical reactions of the body. Beyond physical health, magnesium plays a key role in cognitive functioning and emotional balance.
Beyond the brain, magnesium supports healthy blood flow by relaxing blood vessels. Healthy blood flow ensures efficiency. On a cellular level, magnesium is essential for producing the energy ‘currency’ of the cells, ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
What can be the sign of magnesium deficiency?Research shows magnesium deficiency can impair synaptic plasticity, which is the brain’s ability to form new connections. Synaptic plasticity directly affects learning and memory. Magnesium has also been associated with reducing the risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
- Fatigue and low energy: Magnesium is essential for energy production and its deficiency can leave a feeling of constant tiredness.
- Tremors or twitching: Magnesium deficiency can interfere with proper nerve and muscle function.
- Anxiety or mood swings: neurotransmitters influence mood and emotional stability. Magnesium plays a crucial role in regulating neurotransmitters.
- Poor concentration: Synaptic plasticity, when impaired, can affect learning, memory and focus.
- Difficulty sleeping or insomnia: low levels of magnesium can disrupt sleep quality by affecting sleep-related neurotransmitters.
You may also like

Ladakh L-G reviews security situation in Leh, calls for heightened vigilance

'Police knocked on my parents' door and told them I'd died in Spain'

PhonePe presents affordable insurance against firecracker accidents this festive season

Kerala Woman Loses Lakhs in PPF Interest Due to Minor Over-Deposit, Court Upholds Post Office Decision

Eddie Howe provides injury update on Newcastle star ahead of Arsenal clash







